Beneficiary of the company:
how to identify the shadow owner of the business?
28.02.2026
It's no secret that in addition to the management and participants (shareholders), in many companies there
is
a so-called "business owner", or beneficiary (ultimate beneficiary).
In tax law, in the field of combating money laundering, the beneficiary is a role in the corporate
structure,
it is actually identified with the company itself.
In bankruptcy cases in Russia, the word "beneficiary" is used as one of the synonyms of the person
controlling
the debtor. As a result, the beneficiaries bear secondary liability on an equal basis with the management
and
shareholders of the debtor, with the only difference that the beneficiaries often have assets that can be
foreclosed.
Fearing the negative consequences of their status, beneficiaries are interested in hiding their connection
with the company and take measures to remain in the shadows - they hide behind other companies, powers of
attorney, chains of transactions, foreign jurisdictions.
Who is the beneficiary and how to establish them?
According to the legal definition, a beneficial owner is an individual who directly or through third
parties owns a company (more than 25% in the share capital) or has the ability to control its actions on
other grounds.
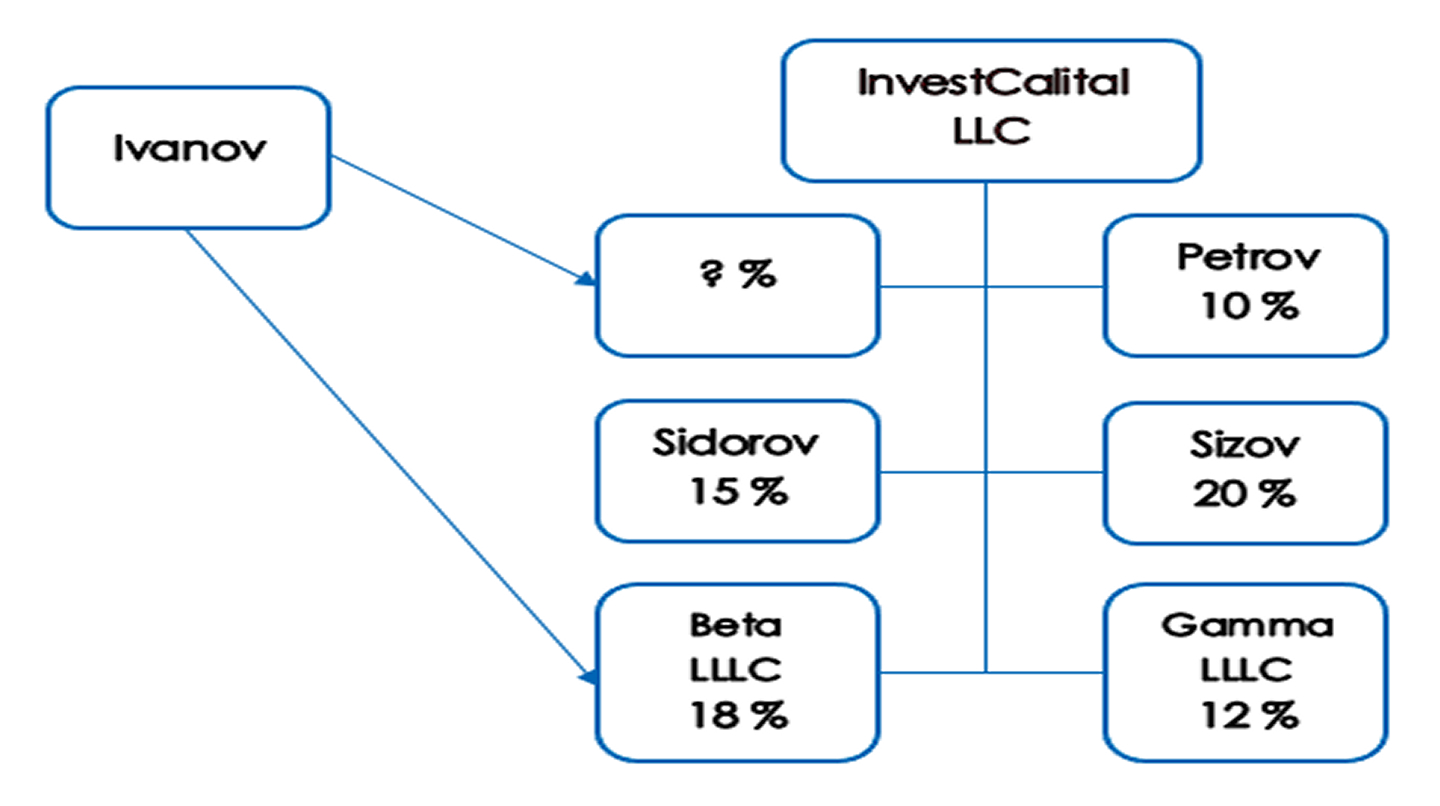
Let's consider the example of InvestCapital LLC.

Ivanov is a beneficiary of InvestCapital LLC (the Company) if:
- Ivanov owns 25% in the Company.
- Ivanov owns 15% in the Company and 100% in Beta LLC - in total, he owns 33% in the authorized
capital of
the Company.
- Ivanov owns less than 25% of the Company, but under a corporate agreement or power of attorney, he
has the
right to dispose of the votes of other members of the Company.
- Ivanov has no share in the Company, but is a charge holder of shares in the Company with the right
to make
a profit, vote on loan agreements with Beta LLC and Gamma LLC (in the amount of 30%).
- Ivanov has no share in the Company, but controls it due to property dependence or personal
connections (he
finances the Company, has family ties with the Company's members).
- Ivanov has no share in the Company, but he determines the areas of activity and/or controls current
activities (coordinates transactions, gives instructions to employees).
Indications of beneficiaries are given in the explanations of Russian state authorities, foreign,
supranational bodies ¹. These indications are also described in judicial practice.
For example, the Commercial Court of the Moscow Circuit in one of its cases stated that "the ultimate
beneficiary may be a former member of the board of directors who does not legally perform his duties to the
company, but actually retains the right to manage business activities and determine the strategic
development of the company" ²
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation highlighted the signs of beneficiary's control over the debtor
³:
- Actions are synchronous without objective economic reasons;
-
The debtor's actions are contrary to its economic interests and lead to a significant increase in the
beneficiary's property;
-
The actions could not have taken place under any circumstances other than when there was control on the
part of the beneficiary.
Thus, in order to identify the beneficiary, it is necessary not only to study the corporate documentation,
but also to identify all the persons associated with it, assess the economic feasibility of the company's
actions, the use of assets, the choice of counterparties and behaviour in the process of concluding and
executing contracts.
¹ Information Letter of Rosfinmonitoring dated 04.12.2018 No 57, Letter of the Federal Tax Service
dated
16.08.2017 No SA-4-18/16148@, Recommendations of the International Financial Action Task Force on Money
Laundering (FATF GAFI) dated 2014 No 24 and No 25, para. 12, 13 of EU Directive No 2015/849/EU.
² Resolution of the Commercial Court of the Moscow Circuit dated 26.12.2016 case No
А4056167/2016.
³ Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 15.02.2018 No 302-ES14-1472.